Training goal
The skills for orientation, exploration and action in space are summarized under spatial orientation. Spatial orientation includes elementary functions such as visual and auditory localization, information about one’s own body position or location in space, spatial knowledge, spatial attention, the comparison of spatial coordinates from different sensory systems as well as the use of currently perceived or stored spatial information for constructive purposes (e.g. drawing, building).
Visual construction performance
The “City Map Game” training helps to improve spatial perception and visuoconstructive performance.
In the first part of the task, a city map is put together from suitable elements. This training helps those affected:
- in the manual construction of length,
- when dealing with the size and orientation of shapes or form elements,
- to use spatial relationships of form elements within a figure, or to use a spatial reference system and
- when dealing with three-dimensionality of shapes and objects.
Visual orientation
Patients with a disturbed visual orientation in two-dimensional space very often lose themselves on a complex stimulus template (e.g. city map). The oculomotor scanning of such stimulus templates is characterized by the lack of correspondence between the eye movement pattern and the spatial structure of the template. The impairment of visual orientation and navigation in three-dimensional space, in known or new surroundings or on maps, is attributed to the loss of spatial or geographical knowledge.
Visual orientation is practiced in the second part of the training. The practitioner will acquire eye movement patterns to find the shortest route from start to finish.
Task description
The task consists of two parts:
- The incomplete city map should be completed.
- The shortest route from start to finish should be planned.
A city map is given. Templates exist in different levels of complexity (depending on the level of difficulty).
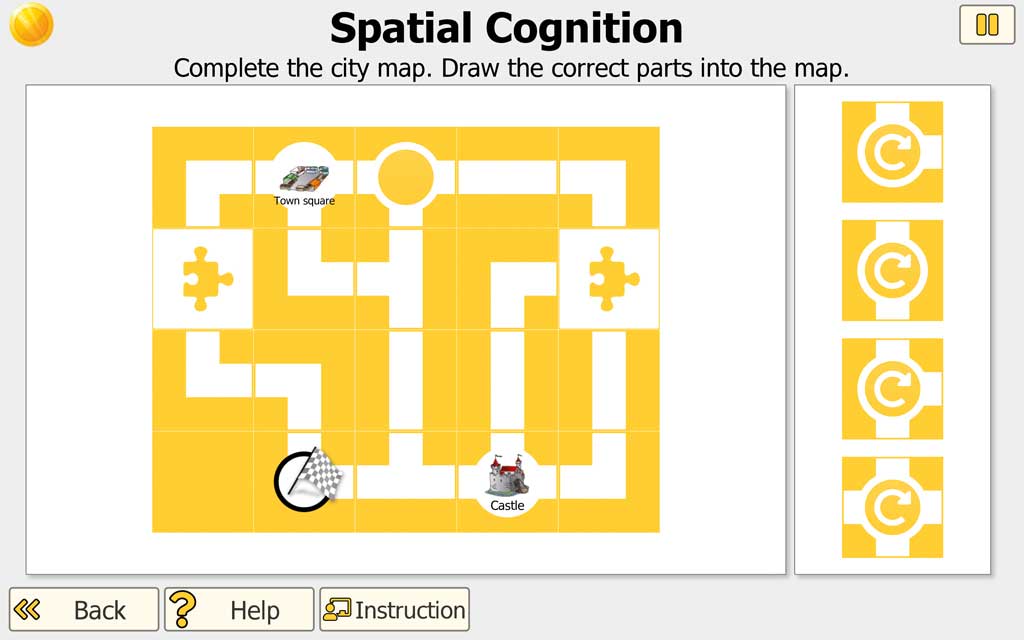
Part 1: Complete the city map
Some parts of the city map are missing. The missing parts should be inserted into the city map.
For low levels: The selection of the cards to be inserted is specified at the edge. The parts do not have to be rotated in order to fit into the plan (rotation takes place automatically). The user pulls the parts from the edge into the gaps in the map.
For higher levels: like part 1, but sometimes the cards have to be rotated to fit into the plan. The cutouts are rotated before or after they are dragged into the free space of the plan. This is done by tapping / clicking, each by 90 degrees. If the map is set correctly so that all streets are correctly connected, part 2 of the task follows.
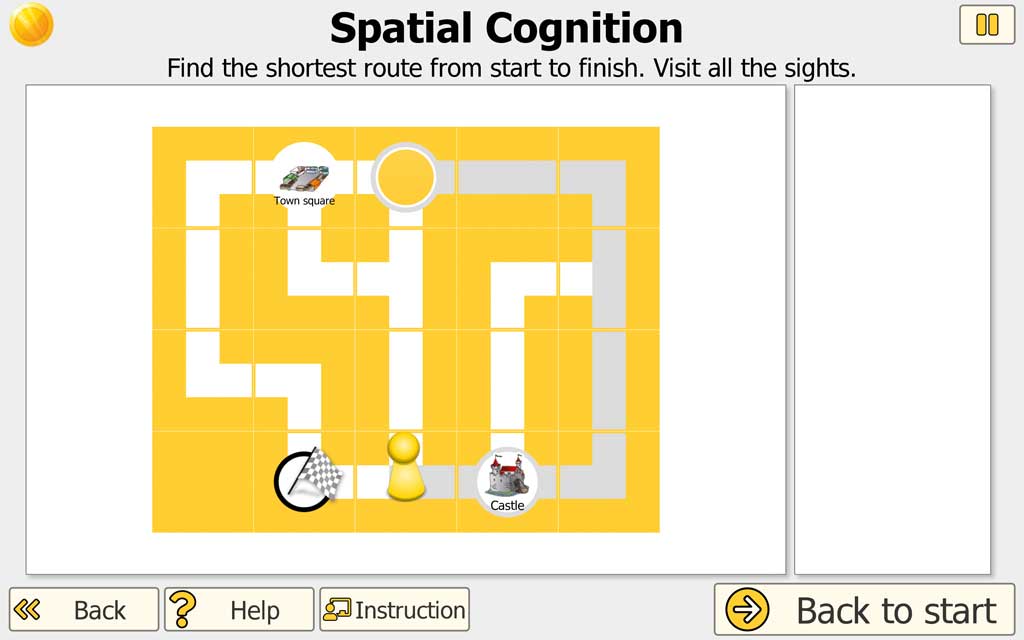
Part 2: Find the shortest route
Sights can be seen on the city map. All sights should be visited on the way from the start to the finish.
A figure and a target flag are displayed anywhere in the map. The task is to guide the character in the shortest way across all sights to the final destination.
In higher levels of difficulty, individual sections of the route are declared as one-way streets. These can only be walked in one direction. The one-way rule applies until the next crossroads. The one-way street arrows are shown after the city map has been completed.
If one have not used the shortest route, the program will report it back. In this case the user can try again to find the shortest route.
Procedure
In the start window for all therapy programs select the “All exercises” area, here the “NEUROvitalis” tab. Click on the training exercise “Spatial Cognition – Vita City”.
A window appears for selecting the level of difficulty and the duration of the training.
Level of difficulty
So that the exerciser does not overwhelm himself, the training begins with a low level of difficulty. All other levels are locked with a lock, which must be opened by completing the previous task.
If a therapist wants to skip levels of difficulty, he can switch on the “Therapist can start all levels” option in the “Patient -> Edit” menu.
Training duration
In general, 20 minutes of training is recommended. A too long training session leads to a loss of attention, the patient makes mistakes and becomes frustrated.
For severely affected people, the training duration should e.g. reduced to 10 minutes (attention span). In this case, several sessions a day make sense.
Progress in therapy
The therapy progress is saved automatically. A new session continues with the difficulty in which the last session ended.
The “Results” window offers various views of the course of therapy (button at the bottom of the “Therapy modules” window).